
Once again for the actual overclocking there are three options. Most overclocking memory requires a 1.65 voltage and in reality there's no reason to go above 1.85 volts, while for general use 1.7 volts is a safe maximum. As guidance the maximum JEDEC recommended voltage is 1.575 and supposedly modules should be able to handle 1.975 volts without permanent damage, though they don't have to function at this level. The stock voltage with DDR3 is 1.5 volts. These offer a way for memory manufacturers to sell overclocking memory and for systems to automatically take advantage of these in a stable manner.Īs with the processor, once you start increasing the clock speed this extra burden on the memory can require increased voltages as power requirements go up. Over recent years both Nvidia and Intel have released their own extensions to these in the form of EPP/SLI-ready and XMP respectively. When your PC posts it'll scan the memory modules for the SPD settings, these hold the default timings for the modules at specific clock speeds.
One thing we've not mentioned are the default SPD settings held within memory modules. The balancing act comes with the fact latency increases to keep timings under control. The alternative way comes from increasing the clock speed, as this simply increase the throughput of the memory. The best results come from reducing the CAS latency which you'll find will release a few per cent of extra performance, as you can see from our results. In reality there's little you can do with the majority of these settings and you'll find you gain little if you try reducing the settings. The amount of time required between memory accesses.Įither T1 or T2 indicating one or two clock cycles and is the time between the memory being activated and when the first command can be sent. How long it takes to disable an active RAS line and activate the next one.
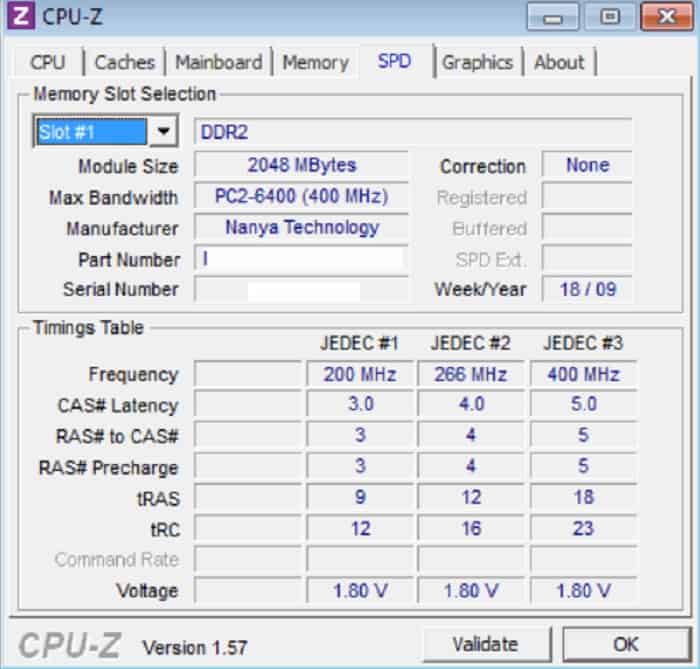
How long it takes to activate a specific RAS line and the subsequent CAS column in memory. The amount of time between the processor asking for data and the memory starting to return it. They are always listed in this order and are measured in clocks:

These describe the amount of time memory requires to perform certain actions. The second area of mystery is the memory timing figures that often go 8-8-8-24 possibly with a T1 or T2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
